什么是ERP? 企业为什么使用它?
企业资源计划 (ERP) 的定义
ERP代表企业资源计划,是指用于计划和管理组织的所有核心供应链、制造、服务、财务及其他流程的软件和系统。企业资源计划软件可用于自动化和简化整个企业或组织的各项活动,例如会计和采购、项目管理、客户关系管理、风险管理、合规性和供应链运营。
单个ERP应用程序可以提供软件即服务 (SaaS),而完整的ERP应用程序套件则可以形成一个ERP系统,用于业务流程的有效通信和整合,以实现应用程序之间的数据流,通常通过现场/本地部署或云中的公用数据库进行。
ERP将企业的各个方面联系起来。利用ERP软件系统,可实现更好的绩效和项目管理,有助于计划、预算、预测和准确地报告组织的财务状况和流程。
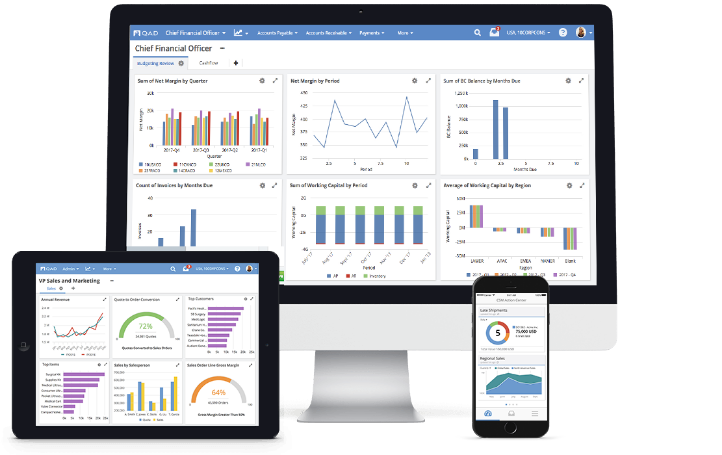
What is an ERP System?
Individual ERP applications can offer software as a service (SaaS), while a complete suite of ERP applications forms an ERP system that can be used to effectively communicate and bring together a variety of business processes. ERP systems enable a flow of data between individual applications, typically through common databases either on-site/on-premise or in the cloud.
ERPs connect every aspect of an enterprise. An ERP software system allows for better performance and project management that helps plan, budget, predict and accurately report on an organization’s financial health and processes. ERP systems have become essential for businesses small, medium, and large across many industries.

ERP系统如何工作?
ERP系统的主要目的是,通过管理和改善企业资源的利用方式来提高一个组织的组织效率。在不牺牲质量和性能的前提下改善和/或减少必要的资源数量,是有效提高业务增长和盈利能力的关键。
ERP系统通常涵盖业务运营的所有方面,通常提供:
- 集成化系统
- 公用数据库
- 实时操作
- 所有应用程序/组件的支持
- 跨应用程序/组件的通用用户接口
- 本地、云托管或SaaS部署
ERP软件具有跨部门收集和比较指标并根据角色或特定用户偏好提供若干不同报告的能力。通过收集的数据,可以加快查找和报告数据的速度,全面掌握资源使用情况,了解企业绩效的全貌。
ERP通过减少维护单独的数据库和电子表格(需要人工合并以生成报告)的需要来同步报告和自动化。这种组合的数据收集和报告功能可提供宝贵的洞察力,例如哪些环节需要削减成本和简化流程,从而提供信息以制定实时业务决策。
ERP系统的类型和ERP软件部署选项
企业资源计划软件被视为一种“企业应用程序”,指的是旨在满足组织的软件需求并提高业务绩效的软件。目前有许多不同的ERP系统,其范围在很大程序上取决于组织的规模、职能和需求。ERP系统的类型通常指的是部署选项,包括云ERP、本地ERP和混合ERP(一些系统部署在云中,一些系统部署在本地)。
每个ERP解决方案系统通常都是量身定制的,以支持业务的不同方面,满足组织的业务要求,并具有不同的部署方法。
大型企业ERP与小型企业ERP
过去,“大型企业ERP”针对的是大型企业,这些企业通常部署现场/本地ERP解决方案,并且有大量资源专门用于IT和其他支持,以分析、定制、升级和部署其软件解决方案。
“小型企业ERP”或“中小型企业ERP”的说法通常指的是具有业务管理应用程序的ERP软件系统,通常是为了满足中小企业的特定需求而创建的。
如今,这些称呼的使用频率越来越低,因为重要的因素不是企业规模,而是确定ERP系统是否能有效地满足当前和未来的业务需求,而不论组织的规模如何。组织考虑并选择的ERP系统必须能够消除昂贵的定制,适应业务快速变化的步伐,应对未来的技术并满足已确定的其他需求,这一点至关重要。
ERP系统的类型:云、本地、混合
ERP系统主要有三种类型,它们具有不同的部署模式选项。最常见的ERP系统类型包括云ERP、本地ERP和混合ERP。
- 本地ERP软件是在现场实施,在组织内的实际办公空间中维护,在企业自己的计算机和服务器上托管的,从而在实施后完全控制、支持和拥有整个系统。
- 基于云的ERP软件是一种基于Web的解决方案,称为软件即服务 (SaaS),指通常通过购买订阅的方式在带有Internet连接的任何设备上访问和存储数据。由软件提供商提供持续支持、更新、培训和灵活的定制。
- “混合” ERP软件是指基于云的ERP系统解决方案与本地部署的ERP系统解决方案的组合实施。托管服务和部署服务的组合因提供商而异。这些模式可以为ERP用户提供在交付模型之间迁移的灵活性,或者整合现有实施中无法获得的优势。
不同的ERP供应商支持不同的部署模式选项。选项的组合通常称为“混合”部署,可以提供托管和部署服务的组合。这些模式可以为ERP用户提供在交付模式之间迁移的灵活性,或者整合现有实施无法获得的优势。
ERP可以用于哪些行业?
ERP软件可用于任何行业,以帮助企业提高效率。它提供了一种有效的通信工具,可以管理内部和外部部门之间的信息,协助日常活动以管理项目,跟踪准则遵守情况,处理业务运营产生的错综复杂的日常事务。
由于ERP起源于制造业,因此有许多强大的行业特定ERP系统来满足各个制造行业的需求。ERP软件系统非常多样化,是许多行业的关键部分,包括但不限于:
-
制造业
-
工业机械及组件
-
建筑与房屋装修
-
电子与科技
-
汽车
-
航空航天与国防
-
医疗保健、制药和生命科学
-
农业综合企业、种植业和农业
-
食品与饮料
-
医疗保健和服务业
-
服装、消费品和零售
随着时间的流逝,ERP系统已经发展为包括对其他应用程序的支持以及可以支持日常业务功能的“ ERP模块”,在许多ERP系统中,这些常见的功能领域被归类为ERP模块,包括但不限于:
- 财务会计
- 管理会计
- 人力资源
- 制造
- 订单处理
- 供应链管理
- 项目管理
- 客户关系管理 (CRM)
- 数据服务
ERP简史
Gartner Group于1990年代首次使用“ ERP”一词,但是,企业资源计划软件和系统已经在制造业中使用了100多年,并且随着行业需求的变化和增长而不断发展。
ERP历史/大事年表:
- 1913年:一位名叫Fort Whitman Harris的工程师开发了经济订货批量 (EOQ) 模型,一种用于生产排程的纸质制造系统。
-
1964年:工具制造商Black and Decker采用了第一个将EOQ与大型计算机相结合的物料需求计划 (MRP) 解决方案。
-
1970年代至1980年代:计算机技术得到发展,概念软件可处理制造业以外的业务活动,包括财务、人力资源数据和客户关系管理 (CRM)。
-
1983年: MRP II被开发出来,它具备“模块”功能并集成了核心制造组件,将制造任务集成到一个公用的共享数据系统中。
-
1990年代至2000年代:Gartner Group创造了“ ERP”一词,以区别于单纯的MRP系统。 ERP系统经过扩展,可以在处理其他功能的同时包含商业智能,例如销售自动化 (SFA)、营销自动化和电子商务。
-
2000-2005年:当ERP软件制造商创建“ Internet Enabled”产品时,基于云的ERP软件解决方案问世,成为传统的本地客户端-服务器模式的替代产品。
- 如今:软件即服务 (SaaS) 和一切即服务 (XaaS)提供了新的ERP交付模式。云ERP解决方案的基于Web的远程访问提供了移动解决方案、安全性并集成了不断变化的行业和智能技术,包括物联网 (IoT)、万物联网 (IoE) 乃至社交媒体,从而为每个行业提供全面的解决方案。
ERP可以应用于哪些行业?
ERP软件可用于任何行业,以帮助企业变得更有效率。它提供了一个有效的沟通工具,可以管理内部和外部部门之间的信息,协助管理项目的日常活动,跟踪准则的遵守情况,并处理日常的错综复杂的业务运行。
由于企业规划软件的根源与制造业密切相关,因此有强大的制造业ERP解决方案,以满足各种特定行业的需求。ERP软件系统是非常多样化的,是许多行业的关键部分,包括但不限于:
- 制造业
- 工业机械和部件
- 建筑和家庭装修
- 电子和技术
- 汽车业
- 航空航天和国防
- 保健、制药和生命科学
- 农业综合企业、耕作和农业
- 食品和饮料
- 医疗保健和酒店业
- 服装、消费品和零售业
随着时间的推移,ERP系统已经发展到包括对其他应用程序和 "ERP模块 "的支持,支持日常业务功能。在许多ERP系统中,这些共同的功能领域被归入ERP模块,包括但不限于:
- 财务会计
- 管理会计
- 人力资源部门
- 制造业
- 订单处理
- 供应链管理
- 项目管理
- 客户关系管理(CRM)
- 数据服务

您的企业何时需要ERP?
业务发展通常以符合企业的短期和长期增长的目标以及对潜在业务挑战的分析为中心。对系统和流程进行定期分析有助于确定企业在什么时候需要集成一个ERP系统。
当现有业务系统和流程出现以下问题时,则应考虑ERP解决方案:
-
无法再运行或效率低下(限制/瓶颈)
-
无法再支持企业的增长
-
缺乏用以减轻风险的当前安全要求
识别损坏的流程对于增长和查找改进环节非常重要。以下是一些查找机会的示例,这些示例可能表示流程不再支持企业的增长:
-
大量使用/依赖单独的数据库/电子表格/程序,需要手工流程进行数据管理,并且经常不同步
-
信息和分析难以访问和/或过时
-
日常流程难以进行或过于耗时,例如基于纸张的会计、财务报告等
-
由于数据不正确或不完整,销售和客户体验受到影响,导致可靠性和服务方面的声誉下降
-
IT流程效率低下/深奥/复杂。当前系统可扩展性差,破碎的系统遗留解决方案
-
IT时间耗费在修复/修补旧系统上,试图跟上增长的步伐
-
不支持物联网、人工智能等先进的新技术
一旦确定了损坏的流程,企业可以采取下一步措施来克服这些业务挑战并支持业务增长。
ERP如何帮助改善和发展业务?
ERP系统用于帮助各种规模的企业克服挑战,从小型企业到大型企业。早期的业务实践可能无法再适应不断增长的需求,需要ERP等更有效的业务工具来有效地管理企业的系统和资源。
ERP软件系统为企业的健康和成长提供了诸多优势。
ERP的优势和业务价值
- 节约成本,提高ROI效率。通过ERP软件提供的集成和自动化功能提高生产力和效率
- 增强业务洞察力。使用单个汇总的数据源和实时数据来改善决策
- 管理合规性。管理和监控法规标准的遵从性,甚至可以针对不遵从情况设置警报
- 减轻和降低风险。实现核心业务运营、手动任务和报告的自动化。减少人为失误,释放员工时间和资源
- 加强协作。打破沟通障碍,实现高效的协作与协调以提高工作效率。提高供应链和销售网络的可靠性。使用需求驱动的MRP预测供需,为订单和供应链的变化做好准备
- 可扩展性。简化操作的一致性基础架构可以随业务一起发展
- 优化客户和合作伙伴管理。利用通过无缝共享信息获得的洞察力进行服务、客户关系管理以及合作伙伴和供应商管理
如何选择ERP系统
挑选和部署ERP系统可能是一项艰巨的任务,需要从众多的软件解决方案当中做出选择。选择ERP系统时,重要的是软件符合您的企业需求和目标,同时具有实施ERP系统所需的支持。
第一次比较ERP系统时,这里有一份快速检查清单供您查阅,这份清单可以帮助您缩小选择范围。

用于选择ERP系统的清单
正在考虑的ERP软件/供应商是否:
- 满足您的系统要求?
- 达到/符合公司目标?
- 可以与当前的现有系统集成/兼容?
- 有用于本地支持的合作伙伴网络/可用性?
- 提供培训/支持选项?
- 有来自客户的参考和建议?
- 持续改进和发展以利用新技术并适应挑战?
将ERP选项缩小到最符合您的当前系统和目标的解决方案,有助于与组织的关键决策者一起评估系统的优势和功能。这些决策者的见解和支持可以促进整个组织对ERP实施的采纳和支持。
What is ERP Implementation?
The process of transitioning to a new ERP system varies by project and requires planning and strategizing to best fit the needs of your company. Choosing the right ERP implementation strategy is key to finding success with your new system. Implementation is an important part of any ERP project. The time and financial investment involved depends on several factors, including deployment model, system complexity, implementation strategy, company sizes and the resources dedicated to the project. Done poorly, an implementation project can eat up valuable resources. Done well, an ERP integration can set your company up for an exciting new level of success. Learn more about the steps of a successful ERP implementation below.
ERP Implementation Steps
At each step in QAD’s scalable ERP system integration process, teams should review all milestones, deliverables, and commitments and report on progress. Our strategy, called Effective On-Boarding (EOB), makes the ERP system implementation fast and easy. This EOB strategy includes the following steps.
-
Plan
During the planning phase, we engage stakeholder groups and form the project team, which will draft a plan with milestones, deliverables, as well as vendor, customer and partner resources. Governance structures such as the Steering Committee and relevant processes around change control, risk, and issue management are agreed upon and set up during this stage as well.
-
Design
Next, we hold business process workshops using built-in process maps designed around major manufacturing industry best practices. During this time, we review how closely the customer enterprise follows these industry standard processes and fill any necessary gaps, which may involve alternative process configurations or designing extensions.
We also gather customer-specific requirements for subsidiary services, such as interfacing, EDI, eInvoicing, etc. and complete the technical work to include those subsidiary services.
At the end of these workshops, we have an agreed-upon functional scope at the process-step and work-instruction level. We then configure our software with those process steps and amend the detailed work instructions accordingly to meet a customer’s specific requirements. Domain and data workshops also occur to identify data structures, cleansing and migration issues. Static data is also loaded into the system.
-
Test
QAD conducts two conference room pilots (CRPs) as well as user acceptance testing (UAT). At each testing step, errors are addressed and should become fewer with each test. The first set of CRPs usually take three to four weeks, with less time needed each round.
-
Deploy
Once UAT is complete, the team plans for the data cut-over and go-live. We draft a detailed plan for when to stop the old system and start the new to minimize any disruption. During go-live, we institute a period of highly focused customer care and support. After this hyper-care period is over and the system is fully handed over to the customer, we conduct an extensive post-project review to ultimately ensure the benefits to the customer have been realized.
ERP Implementation Strategies
There are multiple strategies for a successful ERP system implementation, each with advantages and disadvantages. Here are a few of the most common strategies to consider.
-
Single-Step Method
When using the single-step method, all users move to the new system at once. ERP benefits occur more quickly, but there is a greater risk of errors that can be harder to smooth out later in the process.
With the single-step ERP implementation strategy, you can quickly reap its benefits, such as increased productivity, improved insights, and lower operating costs. This ERP implementation strategy is ideal for users who have strict time constraints and need to complete configuration, testing and training by the projected go-live date.
-
Phased Rollout
In a phased rollout, the deployment of features, tools, and components is carried out over a period of weeks to months. This more measured approach allows for glitches to be caught and addressed more smoothly, but it does take more time to see ERP benefits, and there may be additional costs to maintain two systems at the same time.
Phased rollouts are a safe and effective ERP implementation method. Phased rollouts give organizations more time to learn core functions first and expand from there. This ERP implementation option helps give organizations peace of mind as they iron out any kinks and migrate away from their previous systems.
-
Parallel Rollout
A parallel rollout involves using a legacy system in parallel with the new system for an extended time. Parallel rollouts are typically the least risky way to implement an ERP system because it enables users to revert to a legacy system in the event of any roadblocks. This implementation method ensures that users always have access to vital functions regardless of any problems that occur.
While there is less risk involved given the legacy system is still in operation as a backup, it can be an expensive and time-consuming approach to run two systems.
-
Hybrid Approach
This approach draws from all of the above. A company may choose to do a single-step rollout of one system module but perform a more phased or parallel approach with other more complex or high-stake modules. This ERP implementation approach enables organizations to save time and money on transitioning certain functions while safeguarding vital modules that may require additional troubleshooting.
-
Engage
In this step, we meet with the customer to understand requirements, define the scope of work, set expectations, and identify timing, costs and resources. We then commit to a signed statement of work which acts as the foundation of the project.